
Curious about What is Management Information Systems (MIS)? MIS streamline data flow, ensuring accurate and timely information for better decision-making. By integrating various functional areas, MIS enhances organisational efficiency and coordination, supporting overall strategic goals and operational effectiveness. Let's dive in!
Home Resources IT Security & Data Protection What is Management Information Systems? A Complete Insights to MIS

ISO 27701 Foundation Training Top Rated Course
Exclusive 40% OFF
Enquire Now Download curriclumWe ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

-->
Imagine running a business without any insight into your data—no understanding of customer behaviour, no track of inventory, and no grasp of financial health. This is where Management Information Systems come into play, acting as the central nervous system of an organisation. So, What is Management Information Systems?
By mastering MIS, businesses can transform raw data into valuable insights, driving strategic decisions and enhancing operational efficiency. In this blog, we will explore What is Management Information Systems, its components, and its pivotal role in modern Business Management.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Management Information System?
2) What do Information System Professionals do?
3) Different Types of Management Information Systems
4) Benefits of a Career in Management Information Systems
5) Essential Career Skills of Management Information Systems
6) Management Information Systems Career Paths
7) Future of Management Information Systems
8) Difference Between MIS Departments and IT Management
Management Information Systems encompasses a department within an organisation responsible for managing the hardware and software systems critical for business decision-making. Beyond referring to a department, "MIS" also denotes various types of computer software designed to store, organise, and analyse information.
Today, the term MIS is used in several contexts, including:
1) Decision Support Systems (DSS) software
2) Resource and personnel management applications
3) Project Management tools
4) Database retrieval applications

MIS professionals bridge the gap between business and computing knowledge within organisations. Their roles span various positions, including:
1) Data Analysts/Database Administrators: Manage and optimise data formats, ensuring efficient storage and presentation for decision-making. They may also assist with Data Science projects.
2) Business/Systems Analysts: Improve business processes by translating business needs into technical requirements, often collaborating with IT professionals to develop or implement new systems.
3) Project Managers: Oversee projects by coordinating efforts between data analysts, business professionals, and IT teams, often using Agile techniques.
MIS graduates can also specialise in business domains like accounting, finance, or marketing and may pursue dual majors to enhance their expertise. Their broad skill set equips them to lead technological advancements in various business areas.
Learn to overcome the challenges involved in Information Management with our ISO 27701 Training – Join now!
Here are the four main types of MIS software:
1) Decision Support System (DSS): Analyses business data to help managers make informed decisions. For instance, a DSS can project revenue based on new product sales forecasts.
2) Transaction Processing System (TPS): Handles routine business transactions such as payroll processing, order management in e-commerce, and invoicing.
3) Management Support System (MSS): Organises and stores data, enabling users to generate reports and perform analysis to support business planning. A data warehouse is an example of an MSS.
4) Expert Systems: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is used to offer insights and recommendations by mimicking the expertise of a human specialist in a specific field.
Here are some important benefits of pursuing a career in MIS:
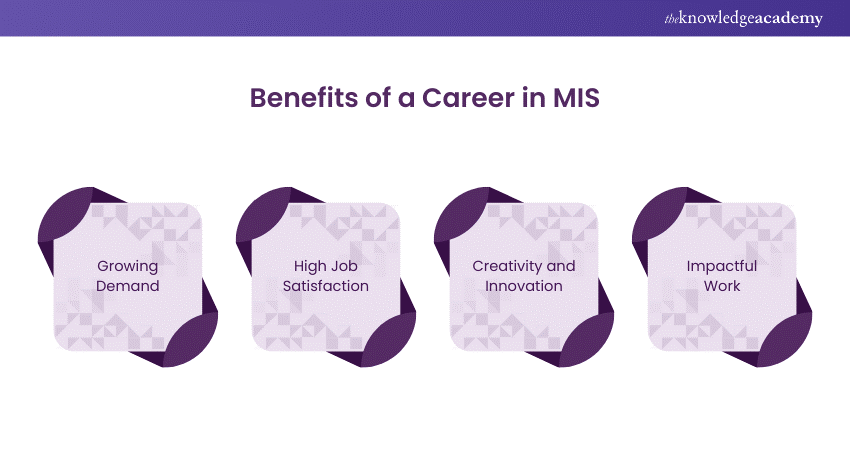
1) Growing Demand: The need for MIS professionals is rising due to advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT), Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, and other emerging technologies.
2) High Job Satisfaction: Many MIS professionals enjoy high job satisfaction due to engaging work, opportunities for creativity, and the chance to make a meaningful impact on their organisation.
3) Creativity and Innovation: This career path offers ample opportunities for creativity, allowing you to develop innovative IT solutions that enhance organisational efficiency and effectiveness.
4) Impactful Work: MIS professionals play a crucial role in improving customer service, boosting sales, and reducing costs, making a significant contribution to their organisations.
Learn how to interpret ISO 27701 requirements for PIMS audits with our ISO 27701 Lead Auditor Training – Register today!
Information Systems (IS) professionals bridge the gap between business and IT, requiring a blend of business acumen and technical skills. Key skills include:
1) Business Acumen: Knowledge in areas like accounting, finance, marketing, and operations to align technology with business needs.
2) Technical Skills: Understanding of programming, database technologies, and emerging fields like Machine Learning and Cyber Security.
3) Analytical Skills: Ability to analyse data and identify trends.
4) Communication: Effectively conveying technical concepts to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
5) Problem-solving: Developing creative solutions for complex issues.
6) Project Management: Managing projects, setting goals, and meeting deadlines.
7) Adaptability: Staying current with evolving technologies and business needs.
8) Collaboration: Working well with diverse teams.
9) Continuous Learning: Keeping skills up to date with industry advancements.
Aspiring MIS professionals can choose their career paths according to their interests. Some of the job roles in this profession include:
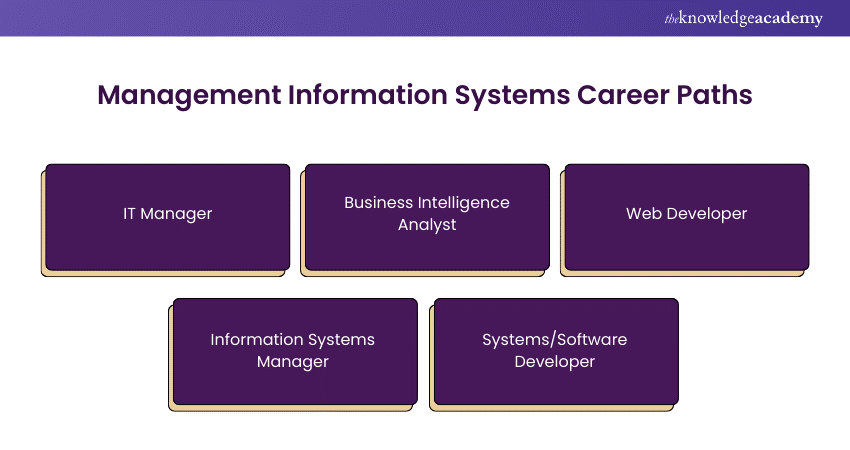
IT managers guide businesses in leveraging information technology to achieve their goals. They successfully bridge the gap between business needs and technological solutions, combining expertise in both areas to drive success.
Business Intelligence Analysts enhance organisational performance by examining business processes and recommending improvements. They possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills and understand various business needs to provide actionable insights.
Web Developers design and build websites and web applications for accessing Management Information Systems. They need strong programming skills and a clear grasp of business processes to gather requirements and ensure effective front-end solutions.
Information Systems Managers ensure an organisation’s IT infrastructure operates smoothly and securely. They oversee the functionality of systems, manage a team of IT professionals, and provide high-quality user support.
Systems/Software Developers create, develop, and maintain software applications. They need strong coding skills and technical expertise. Proficiency in programming languages is essential for effectively executing daily tasks and building robust software solutions.
Currently, MIS professionals utilise enterprise resource planning and business analytics tools to centralise data and enhance decision-making. Looking ahead, the focus will shift to leveraging emerging technologies like AI and blockchain to automate processes and provide deeper insights. MIS professionals will play a key role in advancing digital transformations, automating tasks, and supporting strategic decision-making across industries.
Although the distinction between MIS and IT Management has blurred over time, MIS teams continue to oversee critical systems essential for a company's survival, such as accounting and order entry. They also manage legacy software and hardware, often created by programmers who may no longer be available, sometimes without adequate documentation.
Managing these outdated systems requires a careful approach to modernisation due to associated risks. Despite its less prominent role in contemporary IT discussions, the significance of MIS and the expertise of those who manage it remain crucial. Upper management should recognise the vital role of MIS in maintaining enterprise functionality and driving revenue.
Description
Role of MIS Teams
Oversees critical systems essential for company survival, such as accounting and order entry. Manage legacy software and hardware.
Legacy Systems
Often created by retired programmers with no documentation. Modernisation requires careful handling due to associated risks.
Importance of MIS
Despite being less discussed in contemporary IT, MIS remains crucial for maintaining enterprise functionality and driving revenue.
Management Awareness
Upper management should understand and appreciate the essential role of MIS in the context of enterprise revenue and overall business operations.
MIS involves integrated systems that manage an organisation’s data, ensuring effective decision-making and strategic planning. By understanding What is Management Information Systems, businesses can appreciate its role in improving operations and driving success. As technology continues to advance, the importance of MIS in shaping organisational efficiency will only grow.
Sign up for our ISO 27701 Internal Auditor Training to effectively manage organisational risks and audit framework processes.
The three main areas of an MIS IT organisation are:
1) Data Management, which involves storing and organising data
2) System Development, which focuses on creating and maintaining software applications
3) IT Support, which provides technical assistance and ensures system reliability
What Makes a Good Management Information System?A good Management Information System is characterised by its accuracy, reliability, and user-friendliness. It should integrate seamlessly with existing processes, provide real-time data, and support decision-making with clear, actionable insights.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 27701 Training, including ISO 27701 Privacy Information Management System, ISO 27701 Lead Auditor Training and ISO 27701 Lead Implementer Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the ISO 27001 Roles and Responsibilities.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 27701, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills in IT Security & Data Protection, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.